Did you know that a self-priming pump is indispensable in many applications? Why should you consider investing in one?
Self-priming pumps eliminate the need for additional equipment to evacuate air, making them highly efficient. They are specially designed to handle challenging situations seamlessly.
Introduction to Self-Priming Pumps
In various industrial and commercial applications, the placement of pumps above the liquid level is often unavoidable. Here, a self-priming pump becomes essential.
This scenario demands a pump that can initiate the pumping process reliably.
The self-priming pump effectively expels air from the suction line. Consequently, it draws liquid upward.
It does this by creating a vacuum that forces liquid into the pump chamber.
This innovative design eliminates the need for auxiliary equipment, simplifying the overall system. Thus, your investment in a self-priming pump results in both operational efficiency and cost-saving.
Moreover, self-priming pumps provide versatility across different types of fluids, making them highly adaptable. This flexibility is paramount for ensuring uninterrupted workflows in demanding environments.
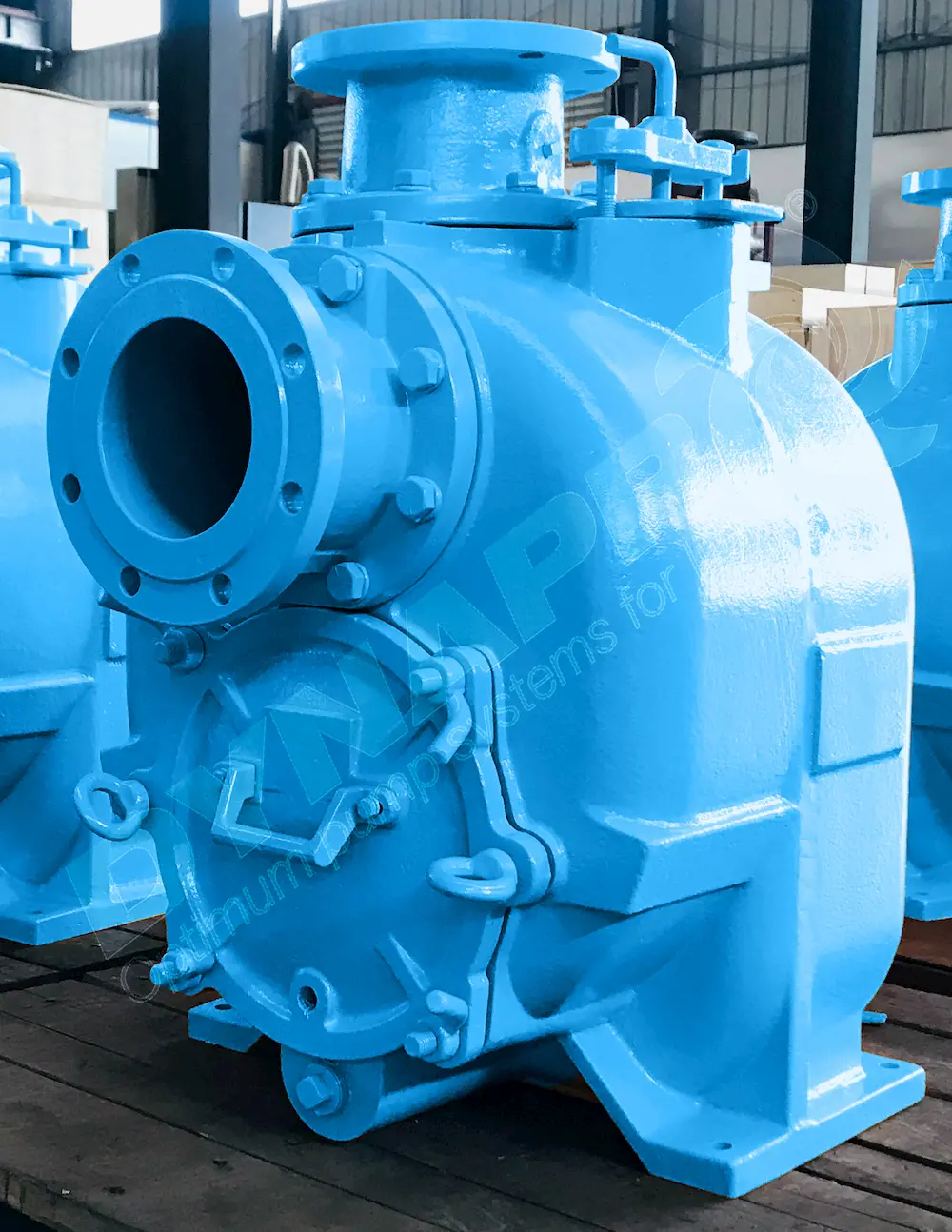

Key Features of Self-Priming Pumps
Self-priming pumps are indispensable in numerous challenging applications.
One key feature is their ability to evacuate air from the suction line. This allows the pump to draw liquid efficiently into the chamber.
The integrated design eliminates the need for secondary pumps or additional equipment, thus simplifying the setup and reducing operational costs.
Moreover, these pumps are designed to handle a variety of fluids. This includes applications involving viscous liquids and those containing small solids.
Their robust construction ensures longevity and reliability, making them a smart investment.
Understanding How Self-Priming Works
A self-priming pump excels by solving the challenge of evacuating air from the suction line efficiently, allowing seamless fluid draw. This innovative capability enables the pump to get to work immediately, without the need for manual intervention, thus boosting productivity.
Initially, the pump operates in its priming mode which involves creating a partial vacuum.
Air is drawn out from the suction line, and a liquid ring forms inside, effectively creating a gas-tight seal. The process continues until liquids replace the air, and normal pumping begins.
Upon achieving full priming, the pump switches to its standard pumping mode. This transition is smooth yet vital, ensuring continuous and optimal performance. Your operations benefit from this technology by maintaining fluid flow integrity, irrespective of the pump’s placement relative to the liquid source.
Benefits of Using Self-Priming Pumps
Self-priming pumps offer multiple significant benefits.
Firstly, the ease of installation is a major advantage. Because these pumps can be positioned above the liquid level, they eliminate the necessity for costly dredging or extensive excavation. Additionally, their self-priming feature reduces the need for ancillary equipment, resulting in lower overall setup costs.
They ensure efficient and prompt operation.
Self-priming pumps excel in operational efficiency – they begin working without manual intervention after startup, ensuring no delay or additional labor is required. This feature minimizes downtime and maximizes productivity.
Lastly, these pumps provide exceptional reliability under varied conditions. Whether you are handling water, chemicals, or slurries, the robust design ensures consistent performance. Their ability to self-prime enhances operational flexibility, making them indispensable for various industrial and commercial applications.
Key Advantages for Industrial Applications
Self-priming pumps find extensive use across multiple industries due to their unique capabilities.
In wastewater treatment facilities, they are indispensable for handling sewage and sludge. These pumps can handle solids and viscous fluids with ease, making them ideal for such challenging environments.
They are also crucial in the agricultural sector, especially for irrigation purposes. By allowing water to be drawn from deep sources without manual priming, they ensure continuous and efficient irrigation practices, essential for crop health.
In the construction industry, self-priming pumps are commonly used for dewatering applications. Whether it’s removing groundwater to create dry foundations or evacuating water from flooded areas, these pumps are reliable under tough conditions.
Their application extends to the marine sector as well, where they are used for ballast water transfer and bilge dewatering, ensuring safety and stability of marine vessels.
Comparing Self-Priming Pumps with Standard Pumps
Self-priming pumps bring a distinct advantage to situations where suction lift is unavoidable. Unlike standard pumps, they can evacuate air and draw liquid into the pump before operation.
Standard pumps, on the other hand, require being placed below the liquid level.
These differences make self-priming pumps indispensable for applications where immediate priming isn’t feasible, such as emptying underground storage tanks or dealing with fluctuating water levels.
By incorporating self-priming features, these pumps eliminate the need for additional equipment and processes typical of standard pumps. In essence, investing in a self-priming pump simplifies installation and reduces long-term maintenance challenges. Once you understand the value, transitioning to self-priming pumps becomes an obvious choice.
Choosing the Right Equipment for your Self-Priming Pump Needs
Selecting a suitable self-priming pump depends on various factors, including application, liquid type, and maintenance ease. Evaluating these criteria ensures optimal performance.
Firstly, consider the pump’s specific application. Different scenarios demand unique specifications.
For instance, handling abrasive liquids will require more robust materials.
Next, ascertain the required flow rate and head. This information is crucial for pump efficiency.
Additionally, assess the pump’s compatibility with the liquid’s chemical composition. Material resistance is essential for longevity.
Finally, do not overlook the pump’s ease of maintenance. Simplified maintenance procedures translate into reduced downtime and prolonged service life.
Installation Guide for Self-Priming Pumps
Correct installation starts with selecting an appropriate location, ensuring the pump’s accessibility and safe connection to power.
For optimal performance, the pump should be as close to the liquid source as possible, reducing the length of the suction line. Minimizing suction lift height is critical to enhance the pump’s efficiency and priming capabilities. Ensure that the suction line is air-tight and properly sealed to prevent air from entering the system during operations.
Additionally, make sure to mount the pump on a stable and level surface. By eliminating vibrations, you enhance its operational stability. Use appropriate mounting brackets and anchors, following the manufacturer’s instructions, to secure the pump firmly.
Finally, always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for priming the pump. Fill the pump casing with liquid to establish the initial prime, and check for any leaks or signs of air ingress. Proper priming is crucial and affects the pump’s longevity and effectiveness, protecting against potential damage caused by dry running conditions.
Practical Tips for Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Maintaining and troubleshooting self-priming pumps is essential to ensure their longevity and optimal performance. Here are some practical tips to help you keep your self-priming pump in top condition:
Regular Inspection and Cleaning
- Inspect Seals and Gaskets: Regularly check seals and gaskets for wear and tear. Replace them if you notice any signs of damage to prevent leaks and maintain efficiency.
- Clean the Impeller and Volute: Debris can accumulate on the impeller and volute, reducing the pump’s efficiency. Clean these components periodically to ensure smooth operation.
Proper Priming
- Ensure Correct Liquid Levels: Make sure the pump’s reservoir is filled with the appropriate liquid before starting. This helps in creating the necessary vacuum for priming.
- Check for Air Leaks: Inspect the suction line for any air leaks. An airtight suction line is crucial for effective priming.
Monitor Operating Conditions
- Avoid Dry Running: Running the pump dry can cause overheating and damage. Always ensure there is enough liquid in the system before operation.
- Temperature Control: In cold environments, drain the pump or provide heating to prevent freezing, which can cause damage.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Blocked Discharge Line: Ensure the discharge line is not pressurized or blocked, as this can impede the pump’s ability to self-prime.
- Excessive Priming Time: Minimize the volume of the suction-side pipework to reduce priming time. Excessive priming times can lead to liquid evaporation and potential dry-running damage.
- Debris in Recirculation Port: If the liquid contains solids, debris may collect in the recirculation port. Regularly check and clean this area to maintain efficient fluid circulation.
Manufacturer Guidelines
- Refer to Manufacturer Instructions: Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for maintenance and operation. This ensures that you are using the pump correctly and can prevent potential issues.
- Use Recommended Parts: When replacing parts, use those recommended by the manufacturer to maintain the pump’s integrity and performance.
By following these practical tips, you can ensure your self-priming pump operates efficiently and has a longer service life. Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are key to preventing downtime and costly repairs.
How to Ensure Efficient Operation
Ensuring the efficient operation of your self-priming pump is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Here are some strategies to help you achieve this:
Proper Installation
- Correct Positioning: Install the pump above the liquid level but within the recommended height limit to ensure effective self-priming.
- Secure Mounting: Ensure the pump is securely mounted to minimize vibrations, which can cause wear and tear over time.
Regular Maintenance
- Routine Inspections: Conduct regular inspections to check for any signs of wear, leaks, or damage. Early detection can prevent major issues.
- Lubrication: Keep the pump’s moving parts well-lubricated to reduce friction and wear. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication intervals and types.
Optimize Suction Line
- Minimize Length and Bends: Keep the suction line as short and straight as possible to reduce resistance and improve priming efficiency.
- Air-Tight Connections: Ensure all connections in the suction line are air-tight to prevent air ingress, which can hinder the priming process.
Monitor Performance
- Check Flow Rates: Regularly monitor the pump’s flow rates to ensure they are within the specified range. Deviations can indicate potential issues.
- Temperature Monitoring: Keep an eye on the operating temperature. Overheating can signal problems such as dry running or excessive friction.
Use Quality Components
- High-Quality Seals and Gaskets: Use high-quality seals and gaskets to prevent leaks and maintain efficiency.
- Proper Impeller Selection: Ensure the impeller is suitable for the type of liquid being pumped. Different liquids may require different impeller designs for optimal performance.
Address Issues Promptly
- Immediate Troubleshooting: Address any issues as soon as they arise. Delaying repairs can lead to more significant problems and costly downtime.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always adhere to the manufacturer’s guidelines for troubleshooting and repairs to maintain the pump’s warranty and performance.
Training and Knowledge
- Operator Training: Ensure that all operators are well-trained in the proper use and maintenance of the pump. Knowledgeable operators can identify and address issues quickly.
- Stay Updated: Keep up with the latest advancements and recommendations in pump technology to continuously improve efficiency.

By implementing these strategies, you can ensure your self-priming pump operates efficiently, reducing downtime and extending its service life. Regular maintenance, proper installation, and prompt troubleshooting are key to achieving optimal performance.
Customer Testimonials and Case Studies
Trusted by industry leaders worldwide.
Numerous customers have found self-priming pumps indispensable. They have praised their efficiency in handling liquid displacement, particularly in challenging conditions like underground storage tanks where a self priming pump excels. Moreover, clients commend the robust construction and reliability, highlighting the substantial reduction in both downtime and maintenance costs.
Positive feedback underscores their practicality.
“The pump’s self-priming capabilities have revolutionized our operations.”
In case studies, one company reported a 25% operational cost reduction – a testament to the pump’s superior efficiency in complex scenarios. In another, a client emphasized the pump’s ability to handle varying liquid consistencies without compromising performance.
These real-world accounts exemplify the transformative impact self-priming pumps deliver. They showcase improved operational workflows, enhanced equipment longevity, and substantial cost savings, affirming the pump’s critical role in successful and sustainable industrial applications.

People Also Ask
What does it mean for a pump to be self-priming?
A self-priming pump can evacuate air from its suction line at startup.
Can centrifugal pumps be self-priming?
Yes, with certain modifications, centrifugal pumps can become self-priming.
What are the benefits of using a self-priming pump?
Self-priming pumps reduce downtime, eliminate the need for additional equipment, and handle challenging scenarios.
How do you maintain a self-priming pump?
Ensure there are no air leaks in the suction line, keep the impeller and volute casing free from debris, and regularly check and fill the priming reservoir. In colder climates, drain or heat the pump to