Once, in the heart of an oil refinery, a sudden vacuum pump failure halted operations, causing immense frustration and significant losses, underscoring the need for reliable auxiliary hydraulic pump equipment. The culprit? Inadequate maintenance, which could have been easily prevented.
Picture yourself in a similar situation where pumping units failure could lead to enormous repercussions.
Ensuring your hydraulic pumping units, including submersible pumps, and auxiliary pump equipment operate seamlessly isn’t just best practice—it’s essential, as all components must work in harmony. With diligent care, you can prolong the life of your machines and prevent costly breakdowns.
1. Types of Pumping Equipment
Understanding the various types of pumping equipment, including submersible pumps, is vital, as each type includes unique components suited for specific tasks.
There are centrifugal pumps which are used for high-flow, low-pressure applications. These pumps work by converting rotational kinetic energy into hydrodynamic energy, making them suitable for continuous operation. Additionally, positive displacement pumps are essential for high-pressure, low-flow scenarios.
Each type has distinct advantages.
Your choice should align with the specific needs of your operation, ensuring the most efficient performance and maintenance routines. This knowledge will also aid in accurately diagnosing and troubleshooting any issues.
By mastering the different pumping equipment types, you unlock the potential to optimize your processes, reducing downtime and fostering a more productive environment. This foresight empowers you to anticipate challenges, keeping your systems resilient and reliable.
2. Selecting the Right Pumping Equipment
Choosing the right pumping equipment can significantly elevate the efficiency and longevity of your operation.
In 2016, a comprehensive study by industry leaders highlighted the intricate nuances involved in selecting the ideal pumping equipment. Your choice of both primary and auxiliary pump equipment heavily influences not only the operational efficiency but also the maintenance requirements and potential downtimes.
First, it’s crucial to assess the specifics of what you aim to move—whether it’s water, slurry, or chemicals. This directly impacts the pump type and its material compatibility, ensuring durable performance over time.
Consider factors such as flow rate, pressure requirements, terrain, and environmental conditions. Aligning these parameters with pump capabilities ensures optimal performance, minimizes energy consumption, and extends equipment life.
Invest your time in detailed research and consultation with industry experts. Choosing wisely now saves you from future headaches.

3. Installation Best Practices
Proper installation is the cornerstone of maximizing the potential of your pumping equipment.
Begin by thoroughly reading and understanding the manufacturer’s manual. This foundational step ensures that you follow the specified guidelines for a successful installation.
Always choose a location free from contaminants and with adequate ventilation. These factors mitigate the risk of damage and extend the life of your pumping equipment.
Ensure that the foundation is level and robust, as stability is paramount. Employ professional technical support if necessary, to guarantee precision.
Secure all electrical and piping connections, double-checking for leaks or imperfections. This final check safeguards against operational interruptions.
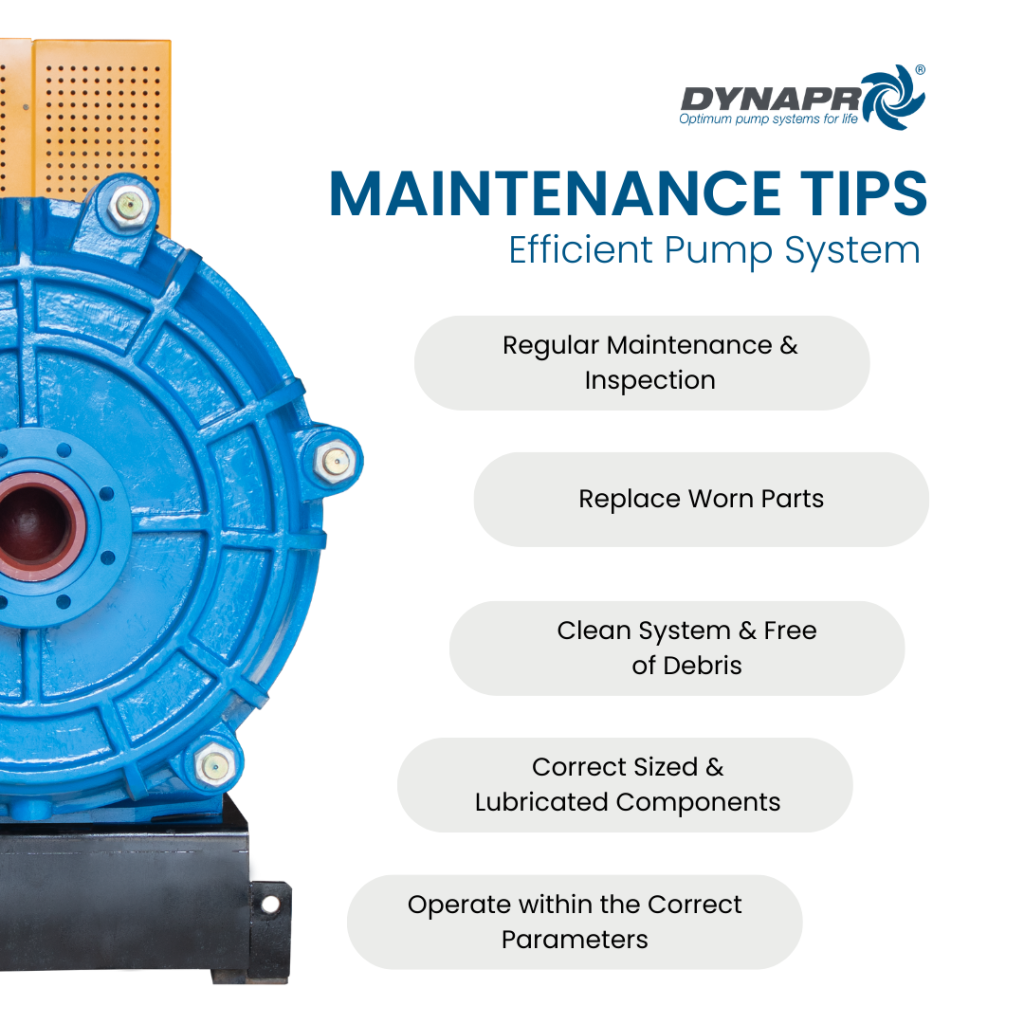
4. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Consistent maintenance fortifies your pumping equipment, ensuring an unwavering operational rhythm. Regular inspections detect early signs of wear and tear, empowering you to take proactive measures before minor issues escalate.
To maintain the efficiency of your pumping equipment, begin with a “baseline check.” This serves as a snapshot of optimal performance, enabling swift identification when anomalies occur. Be meticulous—scan for unusual noises, check fluid levels, and clean filters. Evaluating these aspects routinely will fortify your system’s reliability and safeguard against unexpected downtimes.
4.1 Routine Maintenance Tips
Prioritize regular inspections, focusing on pump alignment, lubrication levels, and wear indicators. Adequate maintenance ensures high efficiency and extends the service life of your pumping equipment.
Incorporate thorough checks on a weekly basis, incorporating tasks like “cleaning filters and inspecting seals.” This level of diligence is a measure that fosters extraordinary equipment performance.
Predictive maintenance can reduce equipment downtime by up to 30%.
Detailed records matter: by documenting each maintenance activity, you create a reliable history that helps anticipate and prevent potential failures. This proactive approach will dramatically boost reliability and operational success.

4.2 Common Issues and Fixes
Even with rigorous maintenance routines, you may encounter issues with your pumping equipment components. How can you troubleshoot these effectively?
In 2023, industry specialists noted a significant increase in efficiency by addressing common problems promptly. Here are some prevalent issues and their respective solutions.
First, if your pump isn’t operating at full capacity, it’s likely due to cavitation. Reducing the pump’s speed or increasing the fluid’s pressure usually resolves this problem.
Second, a leaking pump can heavily impact performance. Inspect seals and gaskets for wear and tear; replacing them often prevents costly downtimes.
Lastly, overheating can halt operations. Ensure sufficient lubrication and check cooling systems regularly. This will mitigate risks and enhance equipment lifespan.
5. Safety Guidelines
Safety is paramount when maintaining pumping equipment.
Accidents happen when safety protocols aren’t upheld. Your first priority should be to wear the proper protective gear including gloves, goggles, and a hard hat. Lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures must be followed to ensure that the equipment is properly de-energized before any maintenance work begins. This minimizes the risk of accidental start-up injuries.
Ensure confined spaces are adequately monitored.
Regular safety drills can prevent many potential hazards – they not only keep your team aware but also prepare them for unexpected occurrences.
Lastly, it is essential to keep a meticulous record of all maintenance activities. Diligent documentation will highlight patterns, preemptively identifying areas needing attention. Your commitment to safety will protect your investment and ensure a secure working environment.
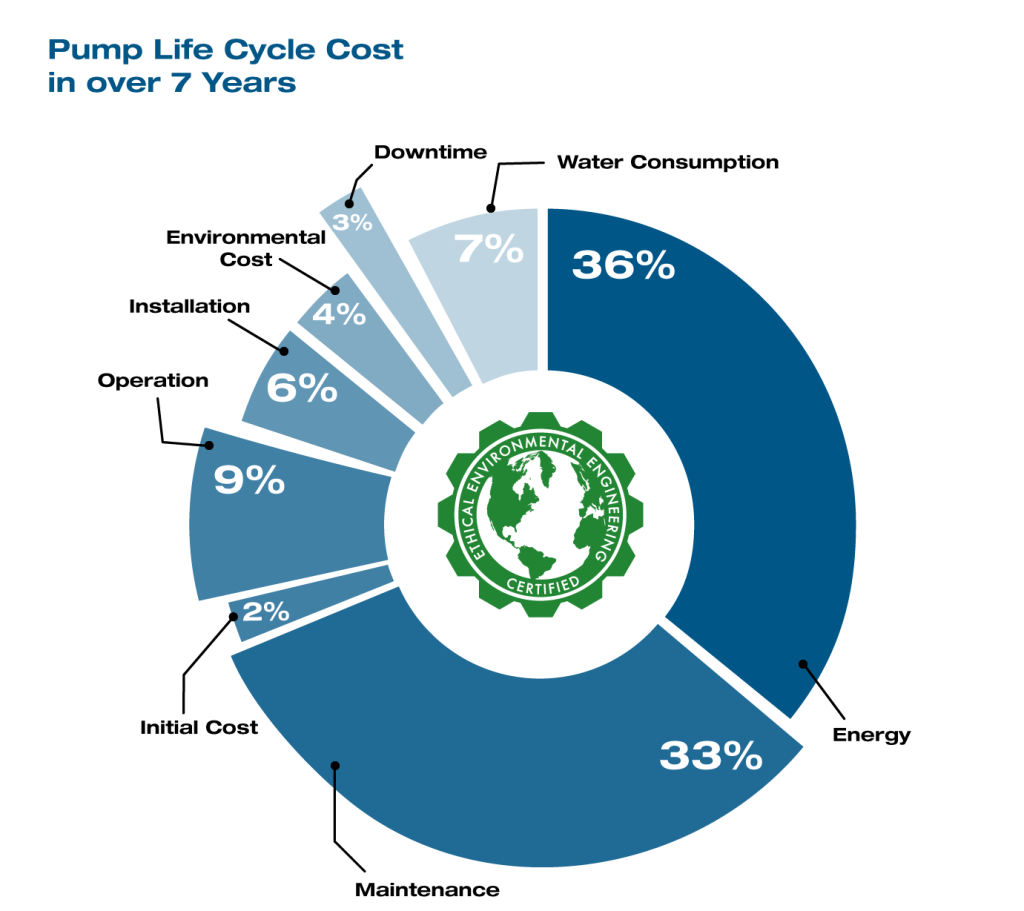
6. Cost Considerations
Maintaining pumping equipment involves both direct and indirect expenses, but careful planning can mitigate costs substantially.
In 2016, industry experts, a notable financial advisory firm, conducted a survey indicating that proactive maintenance can save up to 15% over reactive approaches, which often incur higher repair costs.
Thus, it’s not only about what you’re spending—it’s about where you’re investing. A strategic allocation of resources in regular maintenance can yield significant long-term savings and minimize downtime.
Anticipate the expense of spare parts, labor hours, and potential disruption. Forecasting these categories ahead of time ensures you’re not blindsided by unforeseen expenditures, and aids in effective budget management.
Proactive investment in quality training for your maintenance personnel will also result in fewer costly mistakes.
7. Innovations in Pumping Equipment
Have you ever considered how state-of-the-art advancements could transform the efficiency of your pumping equipment?
In 2016, a groundbreaking technology known as smart pumps emerged, revolutionizing how pumping systems operate. These smart pumps integrate sensors and advanced algorithms, allowing for real-time monitoring and automatic adjustments to optimize performance.
Today, it’s no longer sufficient to rely solely on your equipment’s mechanical efficiency. The advent of IoT (Internet of Things) has introduced unparalleled connectivity, enabling seamless communication between devices and predictive maintenance insights.
Couple these advancements with the advent of energy-efficient designs, reducing not only your operational costs but also the environmental impact. Variable frequency drives, for instance, adjust motor speed to match system demand, further enhancing efficiency.
Innovative solutions like these not only reshape pumping equipment maintenance but also elevate your capability to manage resources efficiently.
8. Industry-Specific Applications
Industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, and pharmaceuticals have unique requirements for pumping equipment. Tailored solutions ensure systems meet stringent regulatory standards, optimizing operations and safeguarding critical processes.
In oil and gas, pumping equipment must withstand extreme conditions, including high pressures and corrosive environments. For water treatment, precision and reliability are paramount to ensure safe and clean water delivery. In pharmaceuticals, maintaining sterile conditions and precision dosage is crucial, highlighting the need for specialized pumping solutions.
Dewatering Pumps
Dewatering pumps are crucial for removing excess water from construction sites and mines, ensuring safe and efficient operations.
- Selecting the right pump guarantees optimal performance and minimizes downtime.
- Regular maintenance extends the lifespan of your dewatering pumps.
- Monitoring for wear and tear helps prevent unexpected failures.
- Adopting modern technology can enhance efficiency and reliability.
- Environmental considerations are essential to comply with regulations.
The effectiveness of dewatering pumps directly impacts project timelines and costs.
By investing in high-quality, well-maintained pumps, you can safeguard your workflow and maximize productivity.